New drone laws Canada have significantly reshaped the airspace, impacting both recreational and commercial drone pilots. These updated regulations, driven by safety concerns and technological advancements, introduce stricter rules regarding registration, licensing, operational limitations, and penalties for non-compliance. Understanding these changes is crucial for anyone operating a drone in Canada, ensuring safe and legal flights.
This guide breaks down the key aspects of the new Canadian drone laws, providing a clear and concise overview of the updated regulations. We’ll cover everything from registration and licensing procedures to operational restrictions and safety guidelines, helping you navigate the legal landscape of drone operation in Canada with confidence.
Navigating the new drone laws in Canada can be tricky, especially with all the recent updates. Understanding these regulations is key before you take to the skies, and a good place to start is by checking out industry news, like this announcement: PROWSE COMMITS TO PRINCETON , which highlights advancements impacting drone technology and safety. Staying informed on both the legal side and the tech side will ensure you’re flying legally and responsibly.
Overview of New Drone Regulations in Canada: New Drone Laws Canada

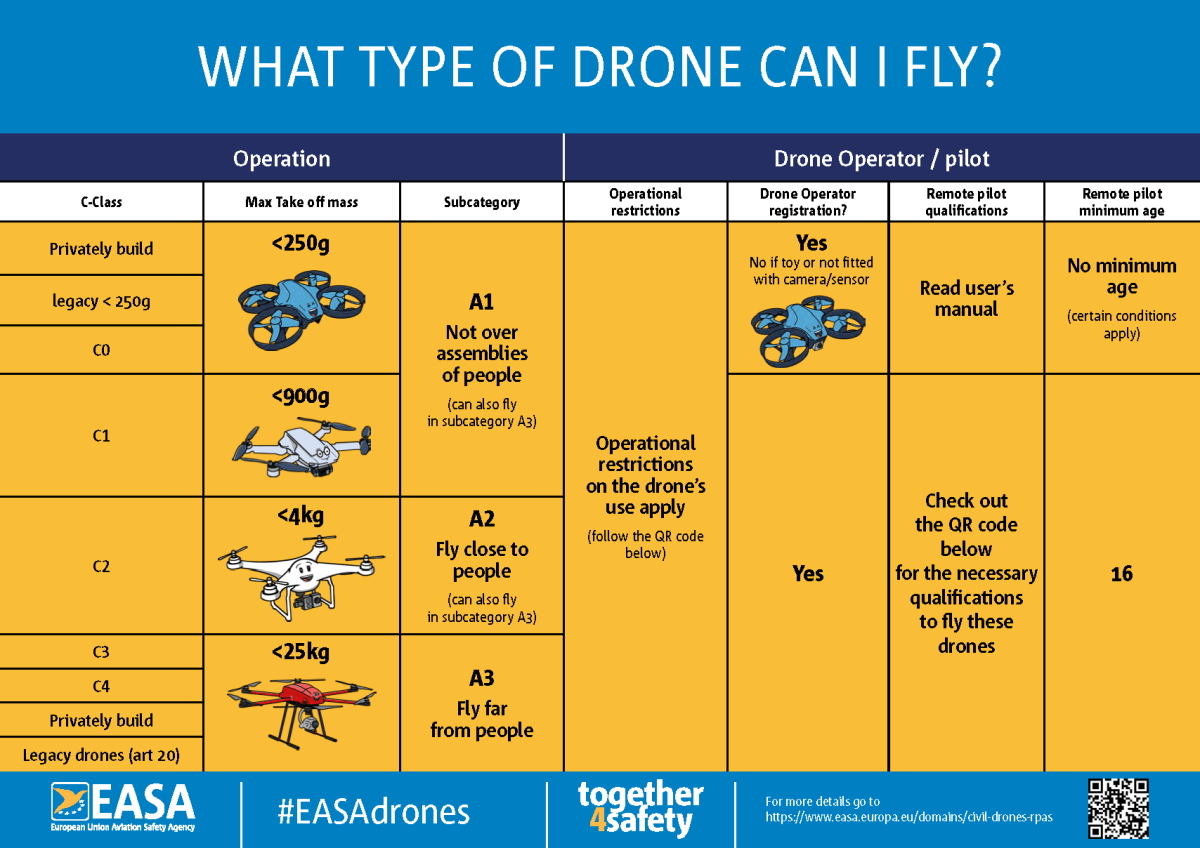
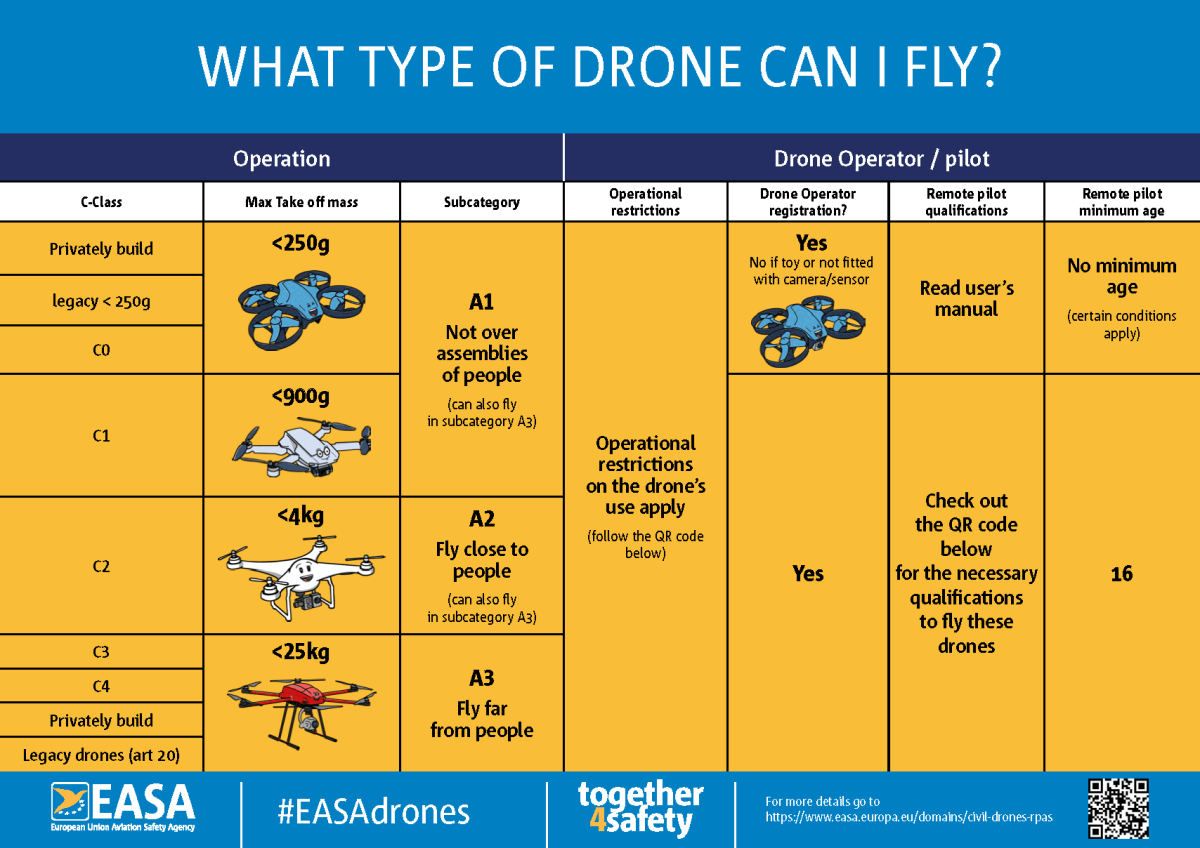
Canada’s drone regulations have undergone significant updates to enhance safety and security. These changes affect both recreational and commercial drone users, introducing stricter rules and clearer guidelines.
The rationale behind these changes stems from a growing number of near-miss incidents and safety concerns related to drone operations. Government reports, such as those published by Transport Canada, highlight the need for more robust regulations to prevent accidents and ensure responsible drone use. The updated laws aim to create a safer airspace for both manned and unmanned aircraft.
The impact on recreational users involves more stringent registration and operational limitations. Commercial users face more rigorous licensing requirements and operational restrictions, potentially increasing costs and administrative burdens. However, the changes also provide a clearer regulatory framework, promoting industry growth and public confidence.
Comparison of Previous and New Drone Regulations, New drone laws canada
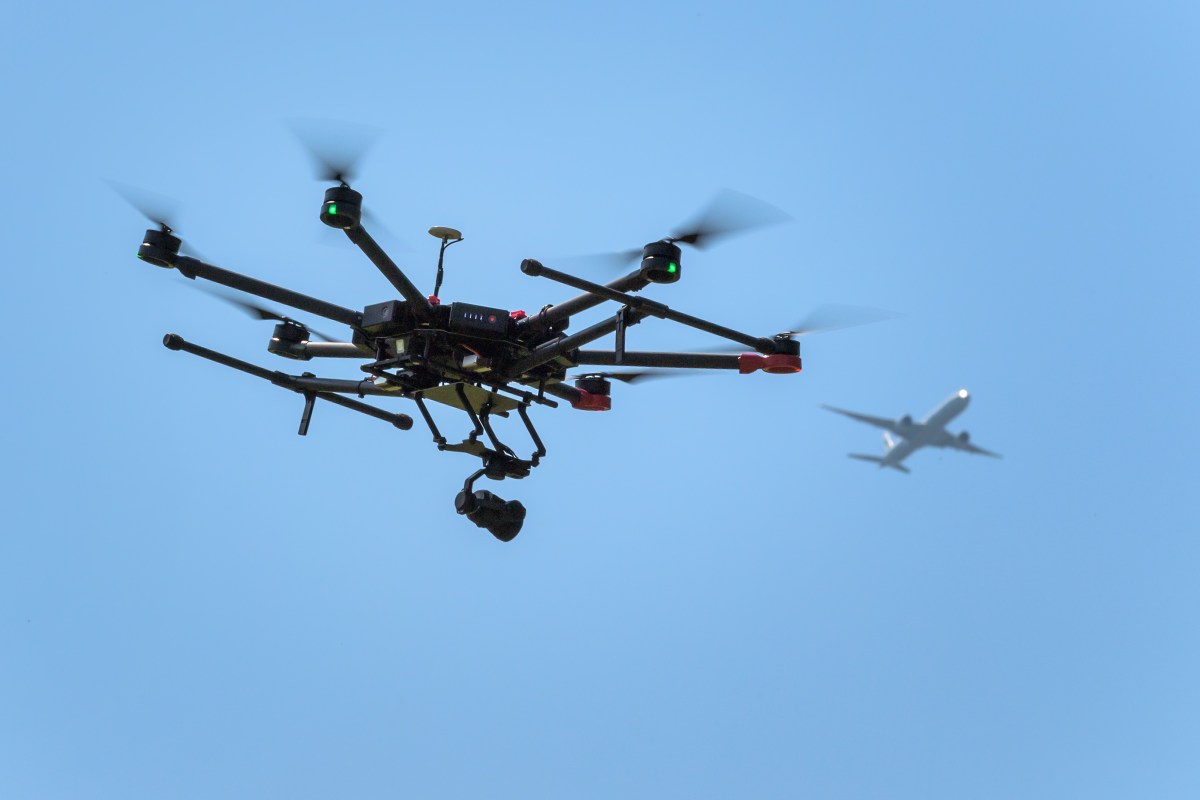

| Regulation | Previous Rule | New Rule | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Registration | Not mandatory for all drones | Mandatory for most drones above a certain weight | Increased accountability and tracking of drone operators |
| Licensing | Limited licensing requirements | Expanded licensing categories based on drone type and operation | Enhanced safety standards and operational expertise required |
| Flight Restrictions | Less specific geographical restrictions | Clearer definition of restricted airspace and no-fly zones | Improved safety around airports and populated areas |
| Operational Limits | Less defined altitude and distance limits | Stricter limits on altitude and distance from the operator | Reduced risk of accidents and unauthorized surveillance |
Drone Registration and Licensing Requirements
Registering a drone in Canada typically involves creating an online account with Transport Canada and providing information about the drone and the owner. Different licensing categories exist, depending on the size and intended use of the drone, ranging from basic recreational permits to advanced commercial licenses requiring extensive training and testing. The process involves completing online applications, potentially undergoing background checks, and paying relevant fees.
Drone Registration and Licensing Process
The process for obtaining a drone license or permit generally involves these steps: 1. Create an account on the Transport Canada website. 2. Provide drone and owner information. 3.
Complete a knowledge test (depending on the license type). 4. Pay the applicable fees. 5. Receive your registration or license number.
Flowchart of Drone Registration and Licensing
A flowchart would visually represent the steps involved in drone registration and licensing, branching based on drone type and intended use, leading to different licensing options and associated requirements. It would begin with the initial assessment of drone characteristics and operator intentions, followed by the application process, examination if required, and finally the issuance of the appropriate license or permit.
Operational Restrictions and Flight Limitations
Several geographical areas are restricted or prohibited for drone flights. These include airports, military bases, and areas with sensitive infrastructure. Drones are also generally prohibited from flying near populated areas unless specific exemptions are granted. Regulations also specify maximum flight altitudes and distances, aiming to prevent accidents and unauthorized surveillance.
Okay, so you’re trying to wrap your head around the new drone laws in Canada, right? It’s a bit of a maze, but think of it like this: you need to know the rules, just like how Barcelona’s Dani Olmo and Pau Víctor needed temporary registration to play. Understanding regulations is key, whether it’s for flying drones or playing football professionally – you gotta follow the rules to play the game!
Examples of Permissible and Prohibited Drone Operations
- Permissible: Flying a small drone in a designated park, maintaining visual line of sight, below the maximum altitude limit, and away from populated areas.
- Permissible: A commercial operator flying a drone for agricultural inspection in a designated area, with proper licensing and approvals.
- Prohibited: Flying a drone near an airport without authorization.
- Prohibited: Flying a drone above the specified altitude limit.
- Prohibited: Operating a drone beyond visual line of sight without the necessary exemptions.
Safety Guidelines and Operational Best Practices
Drone operators must adhere to strict safety procedures, including maintaining visual line of sight with the drone at all times, avoiding obstacles, and performing regular maintenance checks. Pre-flight checks are crucial to ensure the drone is in good working order and all systems are functioning correctly. These procedures are essential to minimize risks and prevent accidents.
Drone Operation Safety Checklist
- Inspect drone for any damage before each flight.
- Check battery levels and ensure sufficient charge.
- Verify GPS signal strength and accuracy.
- Confirm that the flight area is clear of obstacles and within legal limits.
- Maintain visual line of sight throughout the flight.
- Be aware of weather conditions and avoid flying in adverse weather.
- Have a plan for what to do if you lose control of the drone.
Penalties for Non-Compliance
Violating Canadian drone laws can result in significant penalties, including hefty fines, legal action, and potential imprisonment in serious cases. The severity of the penalty depends on the nature and extent of the violation. Past cases involving reckless drone operation or unauthorized flights near airports have resulted in substantial fines and legal consequences for the operators.
Examples of Penalties for Drone Law Violations
| Offense | Penalty | Example Case |
|---|---|---|
| Unauthorized flight near an airport | Significant fine, potential legal action | A hypothetical case involving a drone nearly colliding with a commercial airliner. |
| Operating a drone beyond visual line of sight without authorization | Fine, license suspension or revocation | A hypothetical case involving a drone operator losing control of their drone and causing damage to property. |
| Failure to register a drone | Fine | A hypothetical case involving an operator failing to register their drone, resulting in a fine upon discovery by authorities. |
Resources and Further Information
Transport Canada’s website provides comprehensive information on drone regulations, licensing procedures, and safety guidelines. The website offers detailed FAQs, downloadable manuals, and contact information for inquiries. Other helpful resources include online guides and tutorials focusing on safe and legal drone operation, covering topics such as flight planning, emergency procedures, and maintenance practices.
Impact on Different Drone User Groups
The new drone regulations have varying impacts on different user groups. Recreational users face simpler registration processes, but stricter operational limitations. Commercial operators face more complex licensing and operational requirements, potentially increasing costs. However, clearer regulations create a more predictable environment for industry growth and innovation.
Impact on Specific Drone User Groups
- Recreational Users: Increased awareness of regulations, simpler registration process, but more limited flight options.
- Commercial Operators: More stringent licensing and operational requirements, potentially higher costs, but increased industry legitimacy and public trust.
- Agriculture: Increased efficiency and data collection potential, but higher regulatory compliance costs.
- Photography/Videography: Expanded creative opportunities, but more careful planning and adherence to regulations.
- Construction: Improved safety and efficiency in site monitoring and inspections, but increased regulatory compliance costs.
Final Review
Navigating Canada’s new drone laws might seem daunting at first, but with a clear understanding of the regulations and a commitment to safe operating practices, you can enjoy the benefits of drone technology responsibly. Remember to always prioritize safety, adhere to all regulations, and stay informed about any updates to the law. Safe flying!
Navigating the new drone laws in Canada can be tricky, especially with all the acronyms flying around. For example, you might wonder about the meaning of specific terms, so checking out this article, What does TGL stand for? A pointless investigation (with a , might help clarify some of the jargon. Understanding these details is key to staying compliant with the new regulations and avoiding potential penalties.
Q&A
What’s the maximum weight limit for drones requiring registration?
Generally, drones weighing over 250 grams require registration in Canada.
Do I need a pilot license to fly a drone recreationally?
No, a pilot license isn’t always required for recreational use, but registration is usually necessary for drones exceeding 250 grams. Check Transport Canada’s website for specifics.
What are the penalties for flying a drone near an airport?
Penalties for flying near airports can be substantial, including significant fines and even criminal charges, depending on the severity of the violation.
Where can I find a comprehensive checklist for safe drone operation?
Transport Canada’s website provides detailed safety guidelines and checklists for responsible drone operation. Look for their official publications on drone safety.